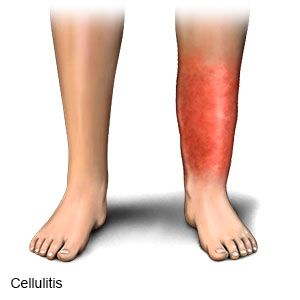
Cellulitis is an infection of the deep layers of the skin. It can occur at any age.
Common symptoms of cellulitis:
- A spreading area of redness of the skin, which is usually warm to touch
- Pain or discomfort at the site
- Swelling of the affected area may occur
- Fever may be present
- They may have swollen glands (lymph nodes) near the area of infected skin.
Video Carousel
Now showing: Video 1 of 1
Causes of cellulitis
Cellulitis often follows injury to the skin, which may be minor, such as a scratch or insect bite. It can also occur following surgery. It occurs more commonly in children with an underlying skin condition (such as eczema) or in children with diabetes.
Treatment
Cellulitis usually responds well to oral antibiotics. Your child should begin to show improvement within two to three days. Treatment with intravenous antibiotics (given into a vein) is very occasionally needed for more severe cases of cellulitis or those that are worsening despite antibiotics being given by mouth. Antibiotics are usually given for a total of 5 days.
If your child has any features of severe infection (amber or red features above), they will need to be urgently seen by a healthcare professional who may decide that your child may benefit from antibiotic treatment.
You can help relieve symptoms by:
- Giving your child paracetamol or ibuprofen if they are in pain or have a fever
- Encourage your child to drink plenty of fluids
Prevention
Not all cases of cellulitis can be prevented, but steps can be taken to reduce the risk of it developing. Cuts, grazes, or bites should be cleaned immediately. Keep the wound covered with a clean plaster or dressing. This will create a barrier against bacteria entering the skin.
Also remember good hand hygiene. Encourage your child to wash their hands regularly and always wash your hands when treating a wound or skin condition.
Feedback Question: Has the advice on this page helped you with a healthcare decision?




